Can You Get Pregnant Without Ovulating? Unpacking The Facts!
What does ovulation have to do with trying to conceive? Seriously, a lot. One’s fertility depends on whether or not they are ovulating.
On Mar 3, 2023 – 12 minutes read

If you’re wondering ‘can you get pregnant without ovulating? then you have come to the right place. Let’s break that down in simple terms. Ovulation refers to the physiological occurrence in which an egg is expelled from the ovary and travels down the fallopian tube, prepared for potential fertilization by sperm. And if all goes well, boom, you are on your way to pregnancy!
Pregnancy is only possible during ovulation when an egg is present and ready to be fertilized. Therefore, monitoring your menstrual cycle and understanding when ovulation occurs is crucial. If ovulation does not occur, there will be no egg available for fertilization and pregnancy will not occur, it is like trying to bake a cake without flour, sugar, or eggs – you need all the ingredients to make it happen. So, keep an eye on your ovulation and you’ll be one step closer to your bundle of joy!
Can You Get Pregnant Without Ovulating? What Signs Indicate Ovulation?
There are many instances when you are unsure about your ovulation cycle. But with simple steps, you can be a pro in understanding what your body is trying to tell you about the conception chances. The likelihood of conceiving can be increased by knowing when you ovulate and by engaging in regular intercourse five days before and on the day of ovulation.

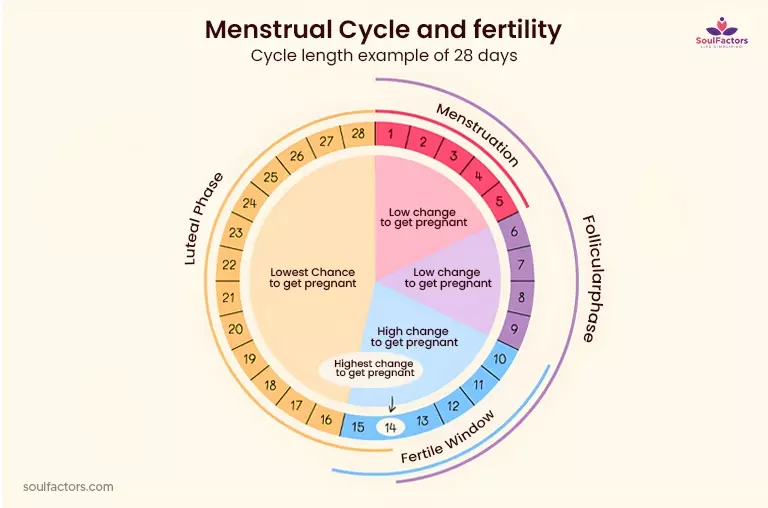
Ovulation usually takes place about 14 days before the beginning of the subsequent menstrual period in a typical 28-day menstrual cycle. However, the cycle duration and the interval between ovulation and the beginning of the following menstrual period may change. If like many women, you have a 28-day monthly cycle, keeping a menstrual calendar might help you figure out your cycle length and when you are most likely to ovulate. If you want to know more about can you get pregnant without ovulating read on.
Common Signs of Ovulation
- Basal Body Temperature: You take your temperature every morning as soon as you wake up, using a technique known as the temperature method (before you get out of bed). In comparison to a standard thermometer, a basal thermometer is more sensitive. To the nearest tenth of a degree, it measures body temperature. During ovulation, the basal body temperature somewhat (increases by 0.5 degrees Fahrenheit). If you monitor your body temperatures before ovulation, you will notice an increase in your basal body temperature. Record your body temperature every day on a tracking sheet to aid planning. You should record your temperature for at least three months before using this technique for family planning.
- Cervical Mucus: The quantity and consistency of your vaginal mucous are altered by hormonal changes during your menstrual cycle. Every day, you must feel and examine your vaginal mucous and note the results on a chart. You likely ovulate (and most fertile) when the mucus is heavy, wet, and slippery. It may have the texture and consistency of raw egg whites.
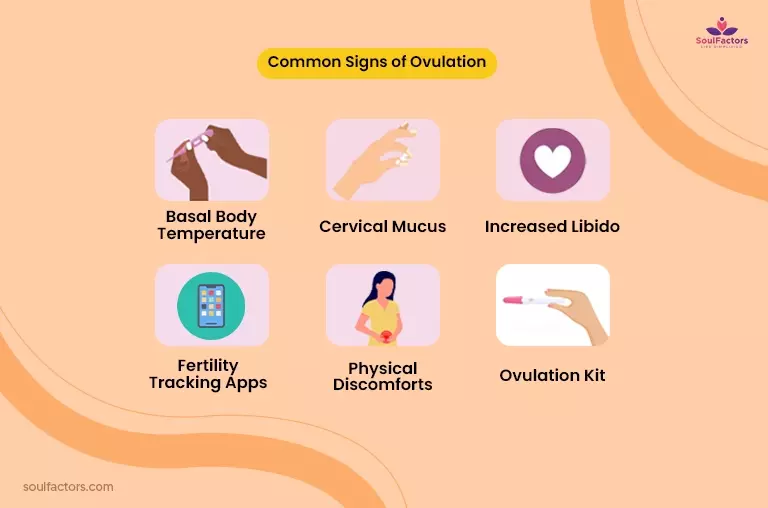
- Fertility Tracking Apps: These apps use algorithms to predict when you are ovulating based on your menstrual cycle, physical symptoms, and other factors.
- Physical Discomforts: Some women experience physical discomforts around ovulation, such as bloating, cramping, or breast tenderness.
- Increased Libido: Ovulation can also result in an increased sex drive for some women.
- Ovulation Kit: This tool you can use at home to anticipate your ovulation is an ovarian cycle prediction kit. If you have regular cycles but are unsure whether you are seeing natural ovulation signals, these tests may be useful (cervical mucus or a rise in basal body temperature). Ovulation prediction kits measure luteinizing hormone levels in your urine. Ovulation will normally take place within 24 hours of the ovulation predictor test becoming positive, suggesting that you are fertile and should have intercourse. These products might not be accurate if you have irregular periods because of polycystic ovarian syndrome.
Since everybody is different, not everyone will experience all of these signs. And while tracking ovulation can help increase your chances of getting pregnant, it is not a guarantee.
If you have concerns or are struggling to conceive, it’s always best to talk to your doctor. So, can you get pregnant without ovulating there you have it! By paying attention to these signs, you will be one step closer to understanding your menstrual cycle and maximizing your chances of getting pregnant.
Can You Get Pregnant Without Ovulating? Your Complete Guide To Fertile Window!
A fertile window is a period in a woman’s menstrual cycle when the chances of getting pregnant are the highest. It is calculated based on when the woman ovulates when an egg is released from the ovary and travels down the fallopian tube, ready to be fertilized. The fertile window typically lasts five days before ovulation and the day of ovulation itself, making it a total of six days in a menstrual cycle.
During the fertile window, sperm can live inside the female reproductive tract for up to five days, so having sex during this time increases the chances of conception. Women can track their menstrual cycles and look out for physical signs of ovulation, such as changes in cervical mucus, basal body temperature, and physical discomforts such as bloating or cramping, to predict when their fertile window will occur.
It is important to keep in mind that every person’s menstrual cycle is unique and can vary in length, so it is always best to consult a doctor to determine the best plan for getting pregnant. If you ask can you get pregnant without ovulating? the simple answer is that by understanding the fertile window, women can increase their chances of conception.
Getting Pregnant In Your Fertile Window
Can you get pregnant without ovulating? If you are trying for a child, you will probably want to take every possible step to conceive. And when it comes to conception, timing is crucial. Research has shown that having sex in the days leading up to and during ovulation, as opposed to the days after ovulation, will increase your chance of becoming pregnant. This is so because eggs only survive after ovulation for up to 24 hours.
Doctors suggest having unprotected intercourse “every other or every day” for 5 days previous to anticipated ovulation, followed by 2 to 3 days after anticipated ovulation. By doing so, she says, “viable sperm will be available when viable eggs are produced.”
Can You Become Pregnant After Your Reproductive Window?
It is of utmost importance to prioritize self-care, regardless of the time you have been trying to conceive or your current plans for starting a family. You should Ease the pressure on yourself by not feeling compelled to engage in sexual intercourse solely during your fertile window. Although this is the period when conception is most probable, there remains a possibility of pregnancy throughout your cycle, even without birth control methods.
Sperms reach maturity five days after sex and can fertilize eggs five days after sex. Sperm can be present and ready when ovulation occurs, even if a woman had sex days before ovulation.
Ovulation dates are frequently estimated, so if your ovulation happens earlier or later than anticipated, pregnancy may occur outside the fertile window.
What To Do If You Don’t Want To Get Pregnant?
There are several methods to protect yourself from getting pregnant, including:
- Use contraception: One of the most effective ways to prevent pregnancy is to use contraception. Many options available includes condoms, birth control pills, intrauterine devices (IUDs), and contraceptive injections. Talk to your doctor to determine which method is best for you based on your lifestyle and health history.
- Have sex during safe days: You can track your menstrual cycle and avoid having sex during your fertile window. This method is not as reliable as contraception, as every women’s cycle length may vary.
- Avoid sexual intercourse: If you are not ready for pregnancy, it’s best to avoid sexual intercourse altogether. This is the most effective way to prevent pregnancy, but it may not be feasible for everyone.
- Practice safe sex: Using a barrier method, such as a condom, during sexual intercourse can help reduce the chances of pregnancy and also protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- Consult with a doctor: Your doctor can provide more information and guidance on the best methods to prevent pregnancy. They can also help you determine the most suitable contraception method based on individual needs and medical history.
Terms To Remember When You Are Trying For Pregnancy
When trying to conceive, there are various acronyms and abbreviations that you may not be familiar with. Here are some of the most frequently used terms you may come across:
- TTC (Trying To Conceive): This acronym is used to describe couples who are actively trying to become pregnant.
- BBT (Basal Body Temperature): This refers to the lowest body temperature that you have in 24 hours. It is taken first thing in the morning and can help track ovulation.
- OPK (Ovulation Predictor Kit): This kit is used to determine when ovulation is occurring. The test measures the level of luteinizing hormone (LH) in the urine, which surges just before ovulation.
- CM (Cervical Mucus): This refers to the fluid produced by the cervix, which changes in consistency and quantity throughout a woman’s menstrual cycle. Monitoring CM can help determine when ovulation is occurring.
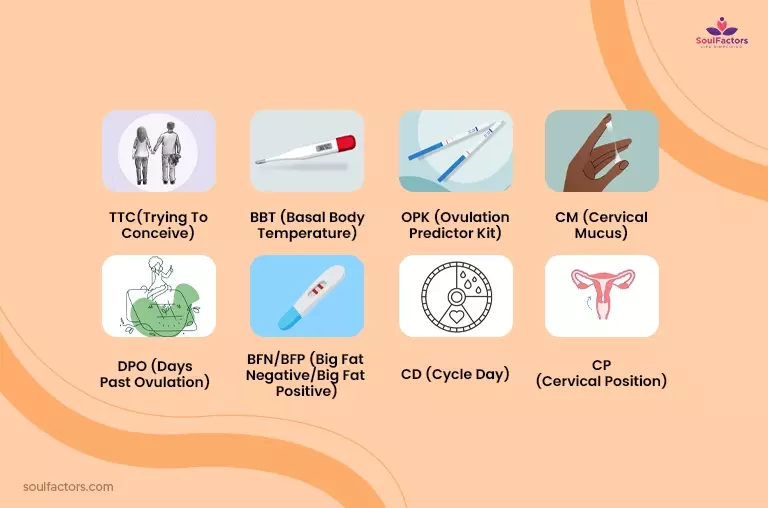
- DPO (Days Past Ovulation): This refers to the number of days that have passed since ovulation occurred. It is used to track pregnancy and fertility.
- BFN/BFP (Big Fat Negative/Big Fat Positive): These acronyms are used to describe the results of a pregnancy test. BFN means the test is negative, while BFP means the test is positive.
- CD (Cycle Day): This refers to the day of a woman’s menstrual cycle, starting from the first day of her period.
- CP (Cervical Position): This refers to the position of the cervix throughout a woman’s menstrual cycle. Monitoring cervical position can help determine when ovulation is occurring.
In conclusion, these are some of the most common acronyms and abbreviations you may encounter when you are trying to conceive. Understanding these terms can help you better navigate the world of fertility and conception.
Anovulation And Its Causes
Anovulation is the term used to describe a menstrual cycle where a woman does not ovulate. Ovulation is the process in which a mature egg is released from the ovary, and it is a crucial step in the process of becoming pregnant. Simply put; Anovulation occurs when the ovary does not release an egg. Some of the causes of anovulation are below:
- Hyperandrogenism: High levels of androgens, also known as hyperandrogenism, can result in anovulation. This occurs when the ovaries produce too much of the male hormone androgen, which can interfere with the normal functioning of the menstrual cycle and ovulation. Conditions that cause hyperandrogenism include polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), congenital adrenal hyperplasia, and adrenal tumors. These conditions disrupt the normal balance of hormones in the body and result in elevated levels of androgens. Symptoms of hyperandrogenism include irregular periods, excessive hair growth, and acne. If left untreated, hyperandrogenism can lead to infertility and other health problems. Treatment typically involves medication and lifestyle changes to manage hormone levels and regulate the menstrual cycle.
- Pituitary gland dysfunction (hypogonadotropic hypogonadism): Pituitary gland dysfunction, also known as hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, is a condition in which the pituitary gland does not produce enough hormones to stimulate the ovaries, leading to anovulation. This can occur due to a variety of causes, including brain tumors, head injuries, or certain medications, and can result in infertility and other health problems. Treatment typically involves hormone therapy to stimulate the ovaries and regulate the menstrual cycle.
- Low levels of thyroid hormones (hypothyroidism, or underactive thyroid): Low levels of thyroid hormones, also known as hypothyroidism or an underactive thyroid, can affect ovulation. Thyroid hormones play a crucial role in regulating the menstrual cycle and reproductive function. When levels are low, it can interfere with ovulation and cause menstrual irregularities. Treatment typically involves hormone replacement therapy to regulate thyroid hormone levels and improve ovulation. Maintaining healthy thyroid function is important for overall health and reproductive success.
- High levels of prolactin (hyperprolactinemia): High levels of prolactin, also known as hyperprolactinemia, can cause anovulation. Pituitary stimulation of milk production is caused by prolactin, a hormone produced by the pituitary gland. When levels of prolactin are elevated, they can interfere with ovulation and disrupt the menstrual cycle. Common causes of hyperprolactinemia (1) include pituitary tumors and certain medications. Treatment typically involves medication to reduce prolactin levels and regulate the menstrual cycle.
- Low levels of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH): GnRH is a hormone produced by the hypothalamus that stimulates the pituitary gland to release follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), which are important for regulating ovulation. When GnRH levels are low, it can disrupt the menstrual cycle and cause infertility. Treatment may involve hormone therapy to regulate GnRH levels and improve ovulation. Maintaining normal GnRH levels is crucial for reproductive health and fertility.
How To Treat Anovulation?
Some of the most common approaches to treat anovulation include:
- Hormone therapy: To regulate hormone levels and improve ovulation, medications such as clomiphene citrate, gonadotropins, and letrozole may be prescribed.
- Surgery: If a physical issue, such as a cyst, is causing anovulation, surgery may be necessary.
- Ovarian stimulation: This technique involves using medications to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs, and increase the chances of ovulation and pregnancy.
- Clomiphene citrate: This medication treats infertility by inducing ovulation in women who are not ovulating naturally.
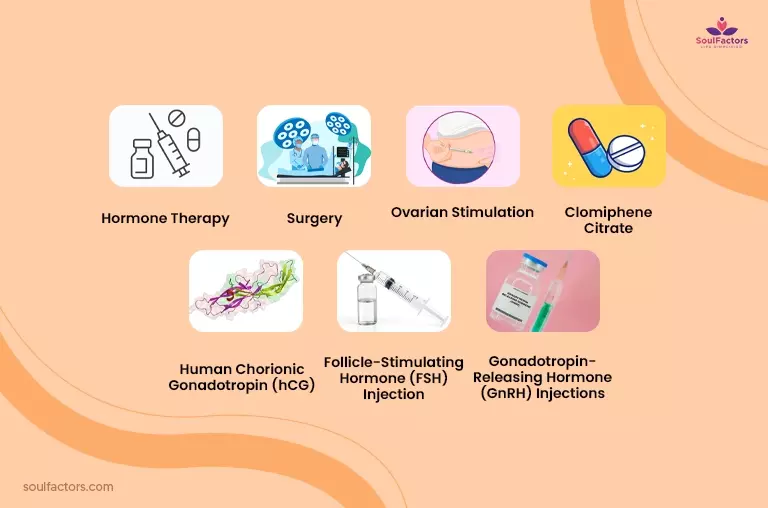
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG): This is a hormone injection used to trigger ovulation in women with anovulation, as part of assisted reproductive technology (ART) treatments such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) (2).
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Injection: This fertility treatment, in the form of an injection, helps to promote the growth of multiple follicles in women with anovulation, enhancing their prospects of a successful pregnancy.
- Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH) Injections: These are administered medications utilized to control or suppress the production of Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and Luteinizing Hormone (LH) in women with anovulation, such as part of a larger assisted reproductive technology (ART) treatment plan.
What Can You Do To Prevent Anovulation?
Preventing or resolving anovulation can be a complex process, but there are steps you can take to increase your chances of ovulating. Here are some preventative measures you can take-
- Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or underweight can disrupt your hormone levels and impact your ability to ovulate. Aim to maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Reduce stress: Stress can interfere with the delicate balance of hormones necessary for ovulation. Try to incorporate stress-reducing activities into your routine, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Avoid alcohol and tobacco: These substances can interfere with hormone levels and reduce your chances of ovulating.
Remember, every woman’s body is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. It is advisable to seek guidance from your healthcare professional to develop a personalized plan of action. So as per our article can you get pregnant without ovulating? with appropriate care and consideration, the likelihood of resolving anovulation and realizing a successful pregnancy can be significantly improved.

Subscribe to Newsletter
Elevate your routine, stay on trend, and embrace a personalized beauty journey with our curated insights.





Write a Comment