Posterior Placenta: Understanding Its Role In Maternal-Fetal Well-being!
Your growing child is dependent on the placenta for the supply of nutrients and oxygen, and the placenta is a genuine miracle of nature. Let’s dissect its scientific significance as well as its nature and function.
On Mar 8, 2023 – 9 minutes read

The placenta, a remarkable product of nature, serves as a vital conduit for supplying nourishment and oxygen to your developing baby. Consider it as your baby’s essential sustenance provider, guaranteeing they receive everything necessary for optimal growth. This organ fosters an extraordinary connection between mother and child. Now, let’s delve into its scientific significance, natural formation, and purpose. The placenta may reside in different positions, including posterior placenta, anterior placenta, fundal placenta, and left/right lateral placenta.
During pregnancy, the placenta undergoes development and assumes a crucial role in nurturing and fostering the growth of your baby. Serving as a vital connection between you and the developing fetus, it provides nourishment and oxygen while removing waste. Additionally, the placenta secretes hormones that contribute to the regulation of your pregnancy. As a transient organ, it exists solely throughout pregnancy and is discharged from your body following delivery.
Placenta formation typically commences within the initial weeks of pregnancy, although the precise timing can vary. It steadily expands and matures throughout the duration of your pregnancy. Monitoring the placenta’s well-being is integral during prenatal care to verify its proper functioning and ensure optimal support for your fetus.
What Is A Posterior Placenta?
The term “posterior placenta” refers to the positioning of the placenta within the uterus throughout your pregnancy. Unlike being affixed to the front or sides, it adheres to the rear wall of the uterus. This occurrence is commonplace and generally does not pose notable complications. Additionally, some believe that the placement of the placenta, whether anterior, posterior, or elsewhere, may be associated with the baby’s gender, although this belief lacks scientific evidence.
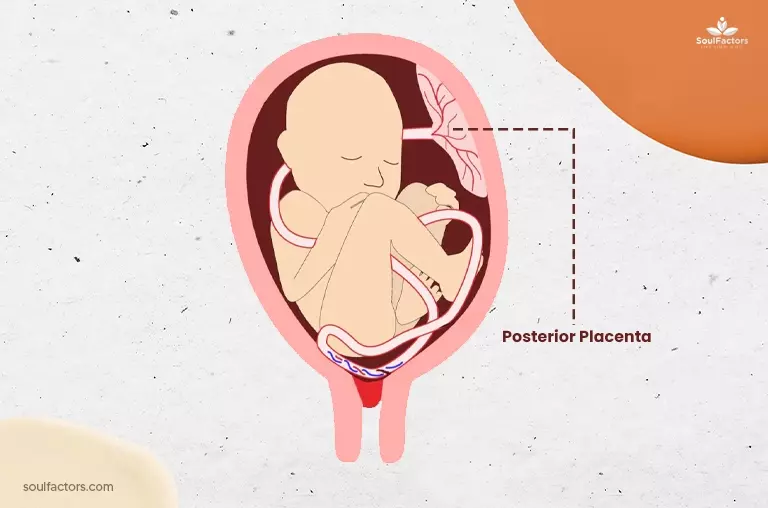
Nevertheless, in certain instances, the presence of a posterior placenta may pose challenges for the fetus to maneuver into the ideal delivery position, potentially heightening the chances of requiring a cesarean delivery. However, it’s essential to note that numerous women with a posterior placenta successfully undergo vaginal deliveries. While this can make it harder for the fetus to move into the optimal position for delivery, it doesn’t necessarily preclude a normal delivery. Consistent prenatal care plays a crucial role in monitoring the placenta’s well-being, ensuring the health of both mother and baby throughout pregnancy.
Development Stages Of Posterior Placenta
Placental formation initiates upon the blastocyst’s implantation in the uterus, where the outer cluster of cells, known as the trophoblast, undergoes development into the placenta. Within the trophoblast, two layers emerge: the inner cytotrophoblasts and the outer syncytiotrophoblasts. These inner cells of the placenta undergo modifications to the uterine blood vessels, facilitating the exchange of blood, and ensuring the fetus receives vital nutrients.
During the early stages of pregnancy, the placenta undergoes formation as the uterus gradually enlarges. This development progresses throughout the pregnancy, with the placenta attaining its full size by the conclusion of the second trimester. Factors like maternal health, fetal conditions, and the positioning of the placenta within the uterus contribute to variations in its size, shape, and thickness from one pregnancy to another. Consistent prenatal care, including regular ultrasound scans, is essential for monitoring the growth and development of the placenta, ensuring its proper functioning, and providing optimal support to the fetus.
Posterior Placenta Grade 1
A posterior placenta grade 1 refers to a situation in which the placenta is attached to the back wall of the uterus, but it does not fully cover the cervix. This is a mild form of the posterior placenta and typically poses no significant risks or complications during pregnancy. However, monitoring your pregnancy and having regular check-ups are non-negotiable to ensure your fetus grows and develops. A grade 1 posterior placenta is considered a relatively common and benign finding during prenatal scans.
Posterior Placenta Grade 2
If the placenta covers part of the cervix and is positioned in the back of the uterus, it is called a “posterior placenta grade 2.” This positioning may occasionally result in pregnancy discomfort, such as lower back pain, and may also raise the possibility of preterm labor or significant bleeding during birth. However, many women with a grade 2 posterior placenta have normal and healthy pregnancies. Women with this type of placenta need close monitoring and regular check-ups to ensure the pregnancy progresses and to plan for safe delivery. In some cases, a planned cesarean section may be recommended to minimize any potential risks.
Is The Posterior Placenta Normal During Pregnancy?
Throughout pregnancy, a posterior placenta is regarded as a typical variation in placental positioning. Serving as a vital organ that nurtures the developing fetus, the placenta typically attaches to the uterine wall. However, in certain instances, it may be affixed to the back wall of the uterus, termed a posterior placenta. This occurrence is common and generally does not present complications for either the mother or the baby. Posterior placenta images can provide further clarity on this natural variation.
However, having a posterior placenta can sometimes lead to back pain or decreased fetal movements felt by the mother. Still, these symptoms can be managed with proper care and monitoring. Overall, having a posterior placenta is considered a normal variation in pregnancy and does not pose significant risks.
Placenta Positions
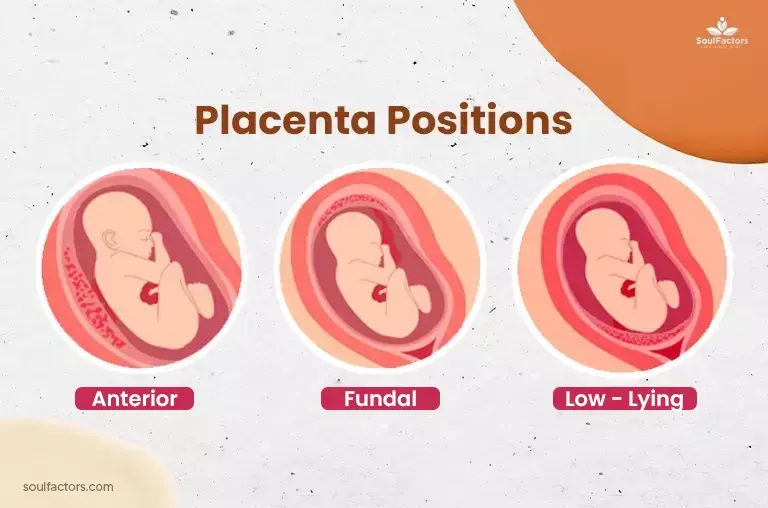
As you’ve gathered, the placenta plays a crucial role in sustaining life during pregnancy. It gracefully maneuvers within the womb, orchestrating a delicate dance to ensure the normal functioning of both you and your baby. With the progression of pregnancy, the placenta strategically shifts to the optimal position for birth. Whether it settles into an anterior, posterior, fundal, or lateral position holds significance in understanding its role. Let’s delve into what each position entails.
- Anterior Placenta: An anterior placenta is affixed to the front wall of the uterus, making it the most prevalent position. While it may diminish sensations of fetal movement for the mother, it typically doesn’t present any risks.
- Posterior Placenta: Conversely, the placenta is attached to the rear wall of the uterus, which is also common and generally benign. However, it may occasionally result in back pain or reduced sensations of fetal movement for the mother.
- Fundal Placenta: A fundal placenta is attached to the top of the uterus, although less frequently encountered, it is not associated with elevated risks.
- Lateral Placenta: The least common position, a lateral placenta, refers to the attachment to the side of the uterus. This positioning can sometimes lead to complications such as preterm labor or a low-lying placenta.
The placental position can vary, and each has qualities and potential hazards. However, most placental placements are considered normal and pose no significant risk to the unborn child or the mother. It is pivotal to have regular prenatal check-ups to monitor the health of the placenta and fetus’s health and address any concerns or issues that may arise during pregnancy.
Complications or Risk of Posterior Placenta
It is important to note that having a posterior placenta is generally considered a normal variation in placenta placement during your pregnancy and does not pose a significant risk for most women.
However, some of the potential complications and risks associated with a posterior placenta are:
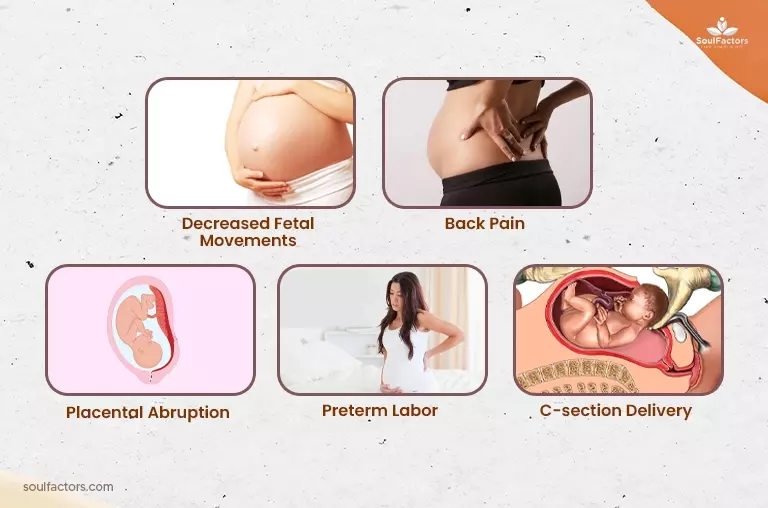
- Decreased fetal movements: You may feel less fetal movement because the placenta can partially cushion the baby’s movements.
- Back pain: It can cause back pain or discomfort for the mother due to its location.
- Placental abruption: The danger of placental abruption is increased when a posterior placenta partially covers the cervix (separating the placenta from the uterine wall). Your cervix goes through subtle changes during your cycle, before and after pregnancy which serves as different indicators.
- Preterm labor: It may increase the risk of preterm labor, which can cause premature birth.
- C-section delivery: It can sometimes make a vaginal delivery more difficult and increase the likelihood of c-section delivery.
Commons Myths About Posterior Placenta
The anticipation of welcoming a new addition to the family is an exhilarating experience for any parent-to-be. Naturally, you may be eager to learn your baby’s gender for planning celebrations like baby showers or gender reveal parties. However, it’s essential to understand that determining gender solely based on the position of the placenta is not entirely reliable. There are various factors associated with this aspect. Let’s break it down for you.
| Myth | Truth |
|---|---|
| 1. A posterior placenta means the baby is in a breech position. | It does not determine the baby’s position. |
| 2. It is a cause for concern. | A posterior placenta is a normal variation in placenta placement and is not inherently problematic. |
| 3. A posterior placenta always causes back pain. | You may or may not face back pain in the posterior placenta. |
| 4. A posterior placenta guarantees a c-section delivery. | You may have a more challenging vaginal delivery, but it is not guaranteed that a c-section delivery will be necessary. |
| 5. A posterior placenta is a sign of a problematic pregnancy. | It is not a sign of a problematic pregnancy in and of itself, but regular prenatal check-ups with a healthcare provider can help monitor the health of the placenta and the fetus and address any concerns or issues that may arise during pregnancy. |
It’s crucial to dispel these misconceptions and provide expectant mothers with the truth regarding a posterior placenta. Women concerned about their placenta’s position should consult their healthcare physician for accurate advice.
Does The Posterior Placenta Mean It’s A Girl Or A Boy?
As an expectant parent, you might be curious about your unborn child’s gender for various reasons, such as planning the nursery or arranging a baby shower. However, it’s common to hear the belief that the position of the placenta can determine the baby’s gender. Nevertheless, this notion lacks scientific backing. The placement of the placenta—be it anterior, posterior, fundal, or lateral—does not indicate the gender of the fetus. Additionally, it’s important to note that while can arise posterior placenta complications, such as potential difficulties during delivery, they are not related to predicting the baby’s gender.
As your pregnancy develops, the placenta’s position might shift, which is not a reliable sign of the fetus’s gender. The only reliable methods for identifying a baby’s gender are ultrasound or genetic testing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
It is normal and usually safe. May cause reduced fetal movement or back pain, but no significant risks.
Placenta position is not a reliable gender predictor. The ultrasound finds genitalia. Genetic tests like chorionic villus sampling, amniocentesis, and prenatal diagnostics can determine gender.
The Placenta position does not indicate gender. Gender determination through ultrasound or genetic testing. The anterior placenta is not exclusive to a specific gender, and fetal gender is independent of placenta location.
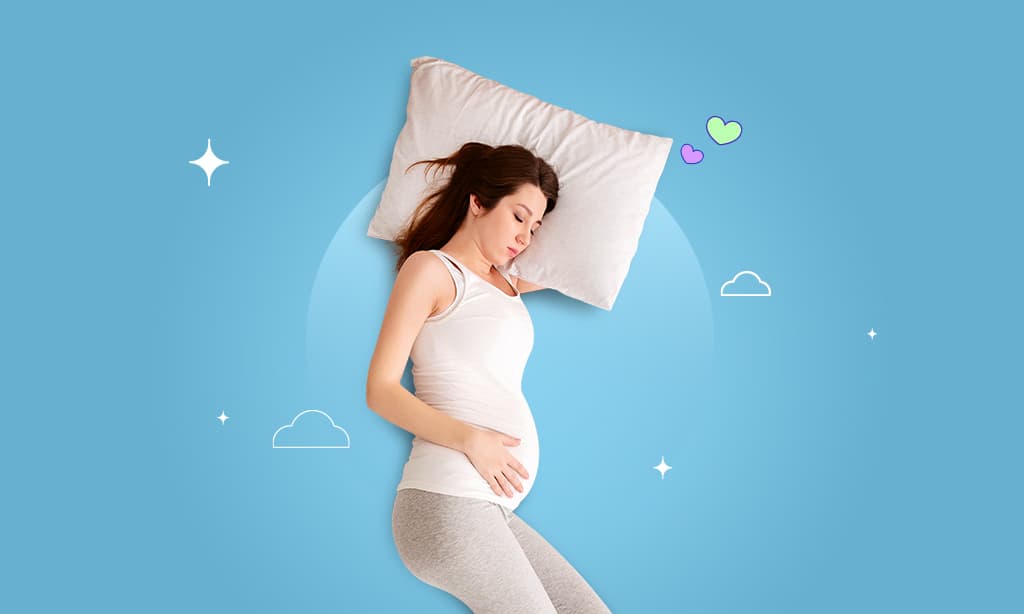
Sleeping on the side, particularly the left side, is the best position for you with a posterior placenta. This position helps improve blood flow to the uterus and the developing fetus, which is paramount for your and your baby’s health and well-being.
You must avoid sleeping on your back since it’s the worst position with a posterior placenta. This position puts pressure on your uterus and decreases blood flow to the fetus, harming you and your baby.
Summary
The posterior placenta is a common variation where it attaches to the back wall of the uterus. While this occurrence typically doesn’t lead to significant issues, it may hinder the fetus from assuming the optimal delivery position, potentially increasing the likelihood of cesarean delivery.
There are two grades of posterior placenta: grade 1, which doesn’t entirely cover the cervix, and grade 2, which partially covers it. Regular monitoring and check-ups are crucial for both grades to ensure a safe progression of pregnancy. Placental formation begins when the blastocyst implants in the uterus and continues to grow throughout pregnancy, reaching full size by the second trimester’s end.
Consistent prenatal care, including ultrasound scans, aids in monitoring the placenta’s growth and function, ensuring adequate support for the fetus. Overall, having a posterior placenta is a normal variation in pregnancy and generally doesn’t pose significant risks.

Subscribe to Newsletter
Elevate your routine, stay on trend, and embrace a personalized beauty journey with our curated insights.





Write a Comment