Does Sunscreen Stop You From Tanning? 9 Tanning Myths Debunked
Curious about whether sunscreen really stops you from getting tanned?
On Oct 28, 2023 – 10 minutes read
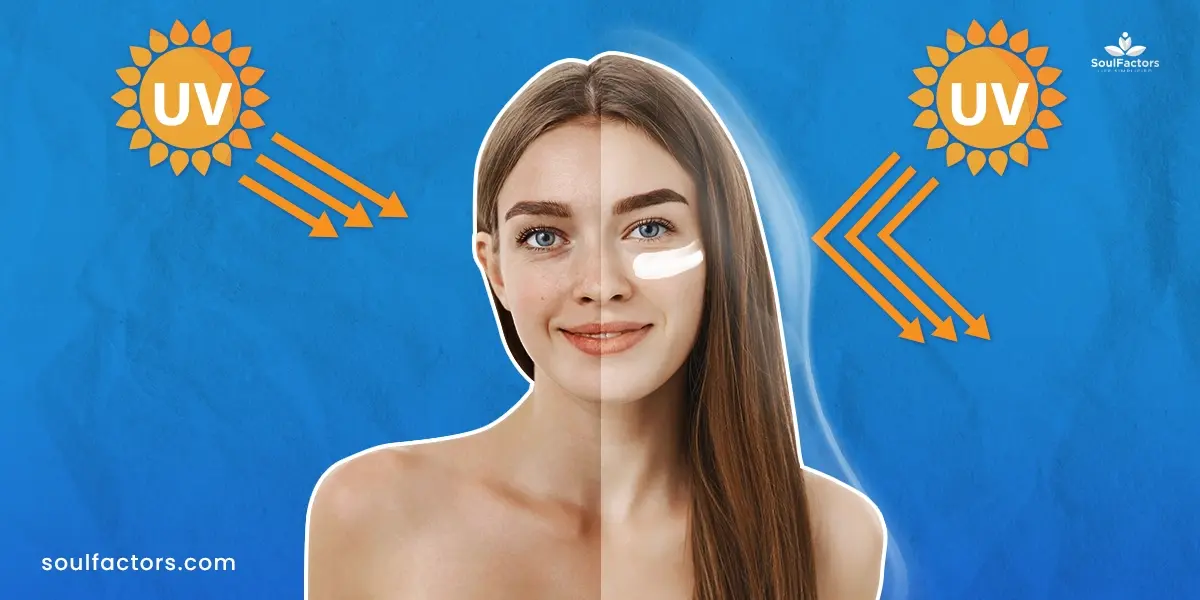

Let’s start with the basics: sunscreen shields our skin from harmful UV rays. Our faces are more sensitive and prone to sun damage, which is why a specially formulated sunscreen for the face is a must. A lot of people want to know, does sunscreen stop you from tanning? because they wish to keep their skin safe from UV rays while maintaining a healthy glow.
So, whether you’re seeking the best sunscreen, looking for sunscreen for your face, dealing with oily skin, or in need of a sunscreen cream, this article will be your ultimate guide.
Importance Of Sunscreen In Protecting The Skin
You might have noticed those little numbers on sunscreen bottles, like SPF 15, 30, 50, or even higher. These numbers represent the SPF rating, which stands for Sun Protection Factor. The SPF rating indicates how well a sunscreen can protect your skin from UVB (ultraviolet B) rays, which are responsible for causing sunburn. The higher the SPF, the better the protection.

- The sun emits both UVA and UVB rays, which can have detrimental effects on your skin. Sunscreen acts as a protective shield, blocking these harmful rays from penetrating your skin.
- Sunscreen, with its SPF rating, helps to prevent sunburn by reducing the intensity of UVB rays that reach your skin.
- Prolonged exposure to UV radiation is a leading cause of skin cancer. Regular use of sunscreen has been shown to lower the risk of various types of skin cancer(1).
- Sunscreen is an excellent anti-aging ally. It helps preserve your skin’s youthful appearance by safeguarding it from the harmful effects of UVA rays.
- Sunscreen is not just for summer days or beach trips. UV rays are present year-round, even on cloudy or overcast days. They can penetrate clouds, so using sunscreen daily is a year-round necessity to ensure your skin’s ongoing protection.
- Some may think that people with darker skin are naturally shielded from the sun’s harmful effects. While it’s true that melanin provides some natural protection, it’s not absolute.
How Does Sunscreen Work To Protect The Skin?
Sunscreen is essentially a protective barrier that acts as a shield between your skin and the sun’s UV rays. Sunscreen works in 2 ways:
- Absorption: Some sunscreen ingredients are designed to absorb UV radiation. When these compounds are applied to the skin, they soak up the UV rays, preventing them from penetrating deeper into the skin.
- Reflection and Scattering: Another set of sunscreen ingredients works by reflecting or scattering UV rays away from the skin’s surface. These are physical or mineral blockers like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide. They sit on the skin and create a protective barrier, bouncing the UV rays back into the environment.
Does Sunscreen Stop You From Tanning? Role Of SPF In Sunscreen Protection
The SPF rating indicates the level of protection a sunscreen offers against UVB rays(2). Here’s how it works:

- SPF 15: This provides moderate protection and is suitable for everyday activities with limited sun exposure. It blocks approximately 93% of UVB rays.
- SPF 30: A common choice for many, SPF 30 sunscreen blocks about 97% of UVB rays and is ideal for extended outdoor activities.
- SPF 50: SPF 50 sunscreen is considered high protection, blocking roughly 98% of UVB rays. It’s recommended for those spending a lot of time in direct sunlight.
- Higher SPF: Sunscreens with SPF ratings higher than 50 are available, but the increase in protection beyond SPF 50 is minimal.
Understanding The Sun’s UV Rays

UVA (Ultraviolet A)
UVA rays are known as “aging rays.” They make up the majority of the UV radiation that reaches the Earth’s surface.
Effects On Skin
UVA rays penetrate the skin more deeply than UVB rays. They are responsible for premature aging, causing wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots.
UVB (Ultraviolet B)
UVB rays are often referred to as “burning rays” because they are the primary cause of sunburn.
Effects On Skin
UVB rays affect the skin’s top layer and can lead to sunburn, redness, and immediate damage. They are also a major contributor to skin cancer, particularly melanoma.
UVC (Ultraviolet C)
UVC rays are the most harmful but fortunately do not reach the Earth’s surface. Blocked by the Ozone layer
Effects On Skin
UVC rays are extremely dangerous to living organisms, but we are protected from them by the Earth’s atmosphere.
HEV (High-Energy Visible) Light
HEV light, or “blue light,” is not a type of UV ray but is worth mentioning due to its potential impact on the skin.
Effects On Skin
HEV light, emitted by electronic screens and artificial lighting, may contribute to skin aging and hyperpigmentation. Protection can be provided through antioxidants and products designed to block blue light.
Does Sunscreen Stop You From Tanning? 9 Tanning Myths: Truth About SPF And Tanning

Myth #1- Sunscreen Completely Blocks Tanning
Truth: Sunscreen helps reduce the risk of sunburn and skin damage, but it doesn’t entirely prevent tanning. It primarily shields the skin from harmful UV rays, offering some level of protection while allowing a gradual tan to develop.
Myth #2- Higher SPF Means No Tan
Truth: Higher SPF sunscreens provide better protection against UVB rays, reducing the risk of sunburn. However, they don’t entirely block tanning. They offer increased defense but don’t entirely stop the tanning process.
Myth #3- You Can’t Tan Through Clouds or Windows
Truth: While clouds and windows reduce UVB exposure, UVA rays can penetrate through them. Even on cloudy days or indoors, UVA rays can reach the skin, leading to tanning and skin damage.
Myth #4- Darker Skin Doesn’t Need Sunscreen
Truth: All skin tones are susceptible to sun damage. While darker skin has more natural melanin protection, it’s not foolproof. Sunscreen helps prevent sun damage and skin cancer, regardless of skin color.
Myth #5- Applying Sunscreen Once Lasts All Day
Truth: Sunscreen effectiveness diminishes over time, especially after swimming or sweating. Reapplication every two hours, or more frequently if in water, is crucial for continued protection.
Myth #6- SPF Above 50 Offers Dramatically Better Protection
Truth: SPF 50 blocks around 98% of UVB rays. Higher SPF values offer only marginal additional protection. Proper application and reapplication matter more than excessively high SPF values.
Myth #7- Indoor Tanning Is Safer Than Outdoor Sun
Truth: Indoor tanning exposes the skin to concentrated UV rays, which can be more harmful than natural sunlight.
Myth #8- Sunscreen Is Only for Sunny Days
Truth: UV rays are present even on cloudy days. Consistent sunscreen use, regardless of weather, protects against sun damage and premature aging.
Myth #9- Using Sunscreen Prevents Vitamin D Production
Truth: While sunscreen reduces Vitamin D production, it doesn’t entirely block it. Brief sun exposure and a balanced diet also contribute to Vitamin D synthesis.
Risks And Benefits Of Tanning With Sunscreen
Tanning while using sunscreen presents a mix of risks and benefits that are crucial to consider for a balanced approach to sun exposure:
Benefits Of Tanning with Sunscreen
- Protection Against Sunburn: Sunscreen is designed to shield the skin from harmful UV rays, reducing the risk of sunburn, premature aging, and skin damage.
- Gradual Tanning: While sunscreen doesn’t entirely block tanning, it helps in achieving a gradual and safer tan by allowing some exposure while providing protection against sunburn.
Risks Of Tanning with Sunscreen
- Misconception of Full Protection: Tanning with sunscreen might lead to a false sense of complete protection. Although it lowers the risk of sunburn, it doesn’t entirely prevent skin damage or skin cancer.
- Prolonged Sun Exposure: Extended periods of tanning, even with sunscreen, increase cumulative UV exposure, which may contribute to skin damage and premature aging.
- Risk of Skin Cancer: Continuous exposure to UV radiation, even with sunscreen, heightens the risk of developing skin cancer, especially with prolonged or intense exposure.
- False Confidence: People might stay in the sun for extended periods due to the misconception that sunscreen provides complete protection, leading to excessive exposure and potential skin damage.
Choose The Right High-SPF Sunscreen
Selecting the right high-SPF sunscreen involves considering various factors, including sunscreen ingredients and the potential benefits when used in combination with Vitamin C serum:

- Broad-Spectrum Protection: Ingredients like avobenzone, zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, or Mexoryl SX provide effective broad-spectrum coverage.
- SPF Value: Opt for a higher SPF, such as SPF 30 or higher, to ensure better protection against UVB rays. Remember, while a higher SPF provides enhanced protection, no sunscreen completely blocks all UV rays.
- Vitamin C Serum: Vitamin C serum, when applied in conjunction with sunscreen, offers added protection. It acts as an antioxidant, helping to neutralize free radicals caused by UV exposure.
- Collagen Synthesis: Vitamin C aids in collagen synthesis, promoting skin repair and reducing the visible signs of aging caused by sun exposure.
Benefits Of High SPF Sunscreens

- Protection from Sun Damage: High-SPF sunscreens provide increased protection against sunburn and skin damage, reducing the risk of premature aging, wrinkles, and skin cancer.
- Improved Skin Health: The combination of a high-SPF sunscreen with Vitamin C serum can enhance skin health by reducing oxidative stress and promoting collagen production.
- Minimized Photodamage: Vitamin C can potentially mitigate photodamage caused by UV exposure when used in combination with sunscreen, contributing to a healthier and more resilient skin barrier.
Can You Still Absorb Vitamin D With Sunscreen On?
Yes, you can still absorb vitamin D with sunscreen on. However, the amount of vitamin D would be small.
Factors That Influence Tanning
- Skin Type and Melanin Production: People with more melanin tend to tan more easily and have a natural defense against UV damage. Those with fairer skin are more prone to sunburn and may tan less or more slowly.
- UV Exposure Intensity and Duration: Prolonged and intense exposure, especially during peak hours, can lead to quicker and deeper tans but also increases the risk of sunburn and skin damage.
- Geographical Location and Altitude: Areas closer to the equator or at higher altitudes have stronger UV radiation, which can lead to faster and deeper tans. Individuals living in such regions might experience more intense tanning.
- Skin Preparation and Sensitivity: Skin that is regularly exposed to the sun tends to tan more easily than skin that has been covered or shielded from sunlight. However, people with sensitive skin are also more prone to sunburn than tanning.
- Use of Sunscreen and Protection: Sunscreen acts as a barrier against UV rays, reducing the skin’s ability to tan. Proper and consistent use of sunscreen decreases the skin’s direct exposure to UV radiation, reducing the tanning effect.
- Genetic Factors: Genetic variations can influence how individuals tan. Some people naturally have a higher predisposition to tan quickly and deeply, while others may struggle to develop a tan due to genetic factors.
- Time of Day and Season: UV radiation varies during different times of the day and seasons. Midday sun exposure generally leads to more intense tanning due to the higher angle of the sun, while seasons with more sunlight can facilitate a deeper and more prolonged tan.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, sunscreen allows for a gradual tan by protecting against sunburn but not entirely blocking tanning.
Sun exposure duration varies; however, unprotected skin can tan in as little as 10-30 minutes, depending on skin type and UV intensity.
Yes, but SPF 50 offers high protection against UV rays, slowing the tanning process while still allowing some color development.
Opt for SPF 30 for moderate protection against sunburn while allowing gradual tanning.
Sunscreen reduces UV exposure but not completely, allowing some UV rays to stimulate tanning while shielding from sunburn.
Sunscreen doesn’t entirely block UV rays, enabling skin to tan gradually while reducing the risk of sunburn.
Final Take
Does sunscreen stop you from tanning? yes! Daily sunscreen is a must! It doesn’t just shield your skin from damage but also helps prevent different types of skin cancers. Studies comparing sunscreen-worn faces with non-sunscreen ones show a big difference over time. You might not see instant changes, but over time, your skin’s texture will improve. With plenty of sunscreens offering extra benefits, pick one based on your skin type and needs, but always stick to using sunscreen.

Subscribe to Newsletter
Elevate your routine, stay on trend, and embrace a personalized beauty journey with our curated insights.




Write a Comment